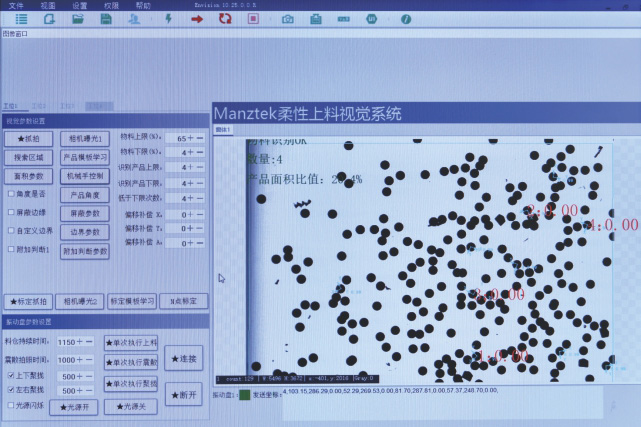
Flexible feeding technology is widely used in the field of industrial automation due to its flexibility and efficiency, especially suitable for handling materials with complex shapes, fragility, or requiring high-precision positioning. The following are its main industry applications and characteristics:
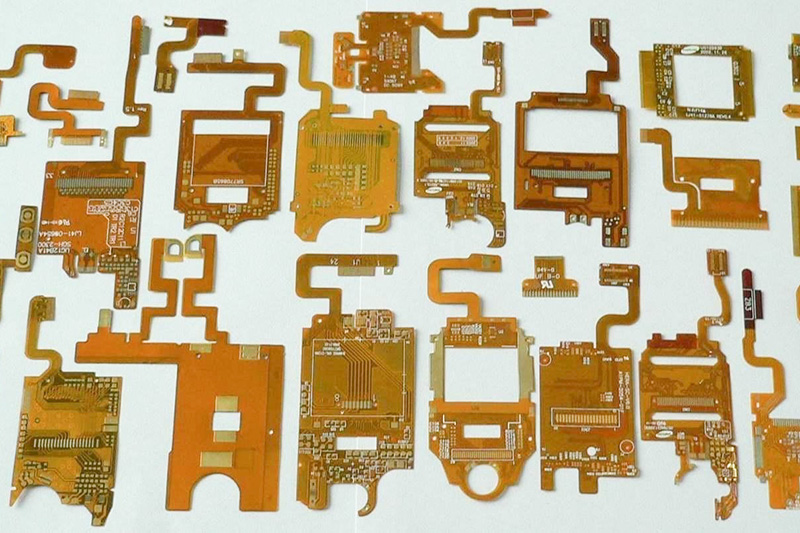
1. 3C Electronics Industry
Application scenarios: mobile phone components (such as camera modules, screens), miniature sensors, headphone components, etc.
Advantages: Suitable for small and lightweight parts, avoiding surface scratches caused by traditional vibration discs, supporting high-speed sorting and assembly.
Case: Apple uses a flexible feeding system in its supply chain to handle the precision assembly of AirPods charging cases.
2. Automobile manufacturing
Application scenarios: Engine small parts (such as gaskets, screws), electronic components (connectors), interior parts, etc.
Advantages: Handling mixed metal and plastic materials, compatible with different batch size changes (such as customized parts).
Case: Tesla factory uses a flexible visual feeding system to assemble heat sinks in battery packs.
3. Medical and Pharmaceutical
Application scenarios: pill packaging, syringe parts, surgical instruments (such as orthopedic screws), testing kits.
Advantages: Compatibility with sterile environment, avoiding contamination; Handle fragile glass medicine bottles or flexible tubing.
Case: Flexible feeding in COVID-19 vaccine production line is used for precise positioning of penicillin bottles.
4. New energy (photovoltaic/lithium battery)
Application scenarios: solar cells, lithium battery electrodes, separators.
Advantages: Non destructive grasping of thin and brittle materials (such as silicon wafers), combined with visual correction to improve yield.
Case: CATL applies flexible feeders in the electrode stacking process.
5. Food and Packaging
Application scenarios: Chocolate, cookie shaped packaging, fresh food (such as strawberries) sorting.
Advantages: Food grade material contact surface, suitable for soft or easily deformed items.
Case: Unilever utilizes flexible feeding automation to package ice cream spoons.
6. Other fields
Hardware: Mixed sorting of screws and springs.
Military aerospace: feeding of precision gears and turbine blades.
Daily chemicals: cosmetic bottle cap, spray valve assembly.
Technical core advantages
Flexibility: By using a visual system and AI algorithm, different materials can be switched without changing hardware.
High yield: reduces jamming or damage caused by traditional vibration, with a yield rate of over 99.5%.
Modular design: supports integration with robotic arms, AGVs, and other equipment to achieve a "black light factory".
Challenges and Trends
Cost: The initial investment is higher than that of traditional vibration discs, but the long-term return is high (with low maintenance costs).
Technology integration: Combining 5G real-time data transmission and digital twin optimization of feeding paths.
Flexible feeding is gradually replacing traditional methods and becoming a key link in intelligent manufacturing, especially with significant advantages in multi variety and small batch production.